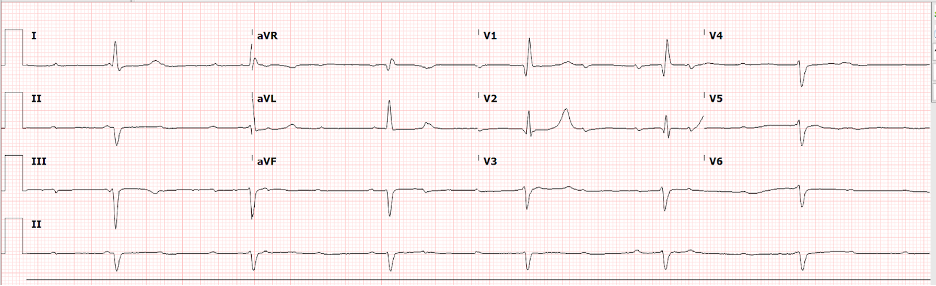
A 74-year-old man presents to the emergency department at a local community hospital after a mechanical fall causing him to be stuck between the toilet and the wall. He is found to have a creatinine kinase of 1600 and creatinine of 1.3. He is treated appropriately for rhabdomyolysis. He subsequently complains of abdominal pain and some dizziness. A CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis shows marked free air and oral contrast extravasation in the right upper quadrant with the site of perforation appearing to be the duodenum. The patient’s vital signs include a blood pressure of 110/65mmHg, heart rate of 50 beats/minute, and respirations 14/min with an oxygen saturation of 98% on room air. An electrocardiogram (ECG) is performed and is shown below.
C) General surgery consultation for consideration of emergent laparoscopic surgery
This patient is suffering from multiple coinciding issues at the same time, and it is important to determine the most important sequence of events. In this case, the patient has a perforation in his abdomen, which is an emergency and requires emergent surgery. Although this patient has a complete atrioventricular block, also known as a third-degree atrioventricular (AV) dissociation (seen in the above ECG), this should not delay surgery and the patient can have a temporary transvenous pacemaker placed at the bedside prior to surgery. Once the patient makes it out of surgery successfully, the need for a permanent pacemaker can be determined with the help of a cardiologist.
Answer choice A: Administer atropine, is incorrect. Administering atropine can be attempted for Mobitz II and complete atrioventricular (AV) dissociation (third degree heart block) but will most likely not be beneficial. Atropine works at the sinoatrial (SA) and AV nodes through its effect on the vagus nerve, but if conduction abnormalities are below the site of action of atropine (as it is in Mobtiz II and third degree heart block), this drug will typically have an insignificant effect.
Answer choice B: Cardiology consultation for ECG interpretation, is incorrect. The patient’s ECG shows a complete AV block that does not require cardiology consultation for interpretation.
Answer choice D: Start a dopamine drip, is incorrect. Dopamine drip can be used in symptomatic bradycardia when atropine is not effective and as chemical pacing when transcutaneous pacing is unavailable.
Answer choice E: Transfer patient for a permanent pacemaker implantation, is incorrect. As noted above, once the patient’s surgical emergency is addressed, cardiology consultation can be obtained for permanent pacemaker placement.
Key Learning Point
An abdominal perforation is surgical emergency, and there should be no delay in taking a patient to surgery.